SYLLABUS
GS-2: Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests; Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests, Indian diaspora; Important International institutions, agencies and fora – their structure, mandate.
Context: Recently, the second India-Arab Foreign Ministers’ Meeting (IAFMM) was held in New Delhi, attended by India’s External Affairs Minister, Arab foreign ministers, and the Secretary-General of the League of Arab States (LAS).
More on the News
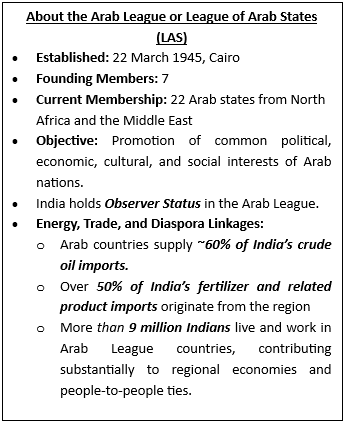
• The IAFMM is the highest institutional mechanism guiding India–Arab cooperation and was convened after nearly a decade.
• The first IAFMM took place in January 2016 in Manama, Bahrain, adopting the Manama Declaration and the Executive Programme (2016–17).
Key Area of Discussion
• Technology, Innovation and Startups: Promotion of partnerships across startup ecosystems, digital technologies, and sectoral applications.
- Advancement of AI cooperation with ethical, regulatory, and governance frameworks, while respecting national sovereignty.
• Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals: Cooperation to provide affordable, high-quality healthcare and medicines.
- India sought recognition of the Indian Pharmacopoeia in Arab countries, subject to domestic regulatory frameworks.
• Space & Youth cooperation: Enhanced exchanges in the space sector to harness space technologies for societal benefits.
- Strengthening youth cooperation through exchanges, capacity building, and participation in cultural and innovative initiatives.
• Peacekeeping & Global Security: Acknowledgment of India and Arab States’ significant contributions to UN peacekeeping operations.
• Emphasis on deeper cooperation through joint training and capacity-building, with Arab Ministers commending India’s initiatives.
• Defence & Counter-Terrorism: The two sides reaffirmed zero tolerance for terrorism, condemned cross-border attacks, and committed to joint efforts against all forms of terrorism, including dismantling networks, countering misuse of technology and drones, and ensuring justice.
- They praised Arab States’ initiatives, Iraq’s and Syria’s roles against Da’esh ( also known as the Islamic State of Iraq) and condemned the Pahalgam attack, emphasising regional security and stability.
- The two sides welcomed the unanimous adoption by the Security Council of the “Algeria Guiding Principles on Preventing the Financing of Terrorism through Emerging Technologies,” at the initiative of Algeria and pursuant to the Council’s 2022 Delhi Declaration on countering the use of new and emerging technologies for terrorist purposes.
- The two sides committed to strengthening cooperation to take decisive and concerted actions against globally proscribed terrorists, terror entities and their proxies, sponsors, backers and financiers, including those in UNSC 1267 Sanctions Committee.
• Regional Issues
- Palestine & Lebanon: Reaffirmed support for a two-State solution based on 1967 borders; welcomed the recently ceasefire in gaza, humanitarian access, UNRWA’s role, and the Arab-Islamic reconstruction plan; supported Palestinian transitional governance arrangements; and reaffirmed support for Lebanon’s sovereignty, exclusive state authority, implementation of UNSCR 1701, and cessation of hostilities.
- Gulf & North Africa: Expressed support for the UAE’s efforts to achieve a peaceful resolution regarding the three UAE islands of Greater Tunb, Lesser Tunb and Abu Musa; reaffirmed support for a Libyan-led political process, national unity, sovereignty, and early presidential and parliamentary elections.
- Horn of Africa & Sudan: Reaffirmed support for Sudan’s sovereignty, unity, territorial integrity, humanitarian access, and rejection of parallel entities; and reaffirmed respect for Somalia’s sovereignty, unity, territorial integrity, and internationally recognised borders.

