SYLLABUS
GS-3: Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilisation of resources, and growth.
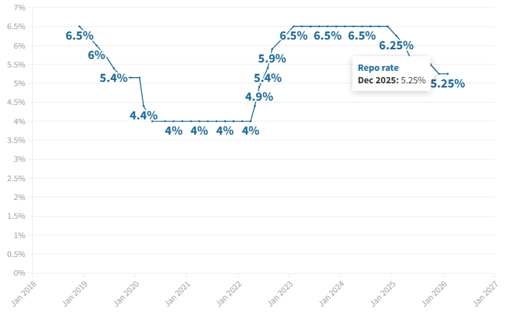
Context: Reserve Bank of India (RBI) announced that the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) has unanimously decided to keep the policy repo rate unchanged at 5.25%, while maintaining a neutral policy stance.
More in the News
Policy Rates & Stance:
• The Standing Deposit Facility (SDF) rate remains at 5%, while the Marginal Standing Facility (MSF) rate and the Bank Rate continue at 5.5%, keeping the liquidity corridor unchanged.
• The RBI reiterated that future monetary policy actions will be guided by incoming macroeconomic data, including inflation data based on the revised CPI series, and the evolving growth outlook.
Inflation Outlook:
• CPI-based retail inflation for FY26 is projected at 2.1%, within the RBI’s tolerance band of 2–6%.
• Inflation is expected to rise gradually due to unfavourable base effects, with projections of:
- Q4 FY26: 3.2%
- Q1 FY27: 4.0%
- Q2 FY27: 4.2%
• Provisional data shows headline CPI inflation at 1.33% in December 2025, providing comfort to policymakers amid global uncertainties.
Growth Projections:
• The RBI revised upward its GDP growth outlook, reflecting resilience in domestic demand:
- FY26: 7.4% (earlier 7.3%)
- Q1 FY27: 6.9%
- Q2 FY27: 7.0%
• Full-year FY27 growth projections will be released after the new GDP series is notified.
Liquidity & External Sector:
• System liquidity averaged around ₹75,000 crore on a daily basis, with the RBI remaining proactive in liquidity management.
• Forex reserves stood at a comfortable $723.8 billion by end-January, strengthening external stability.
Regulatory & Developmental Measures:
• RBI proposed compensation of up to ₹25,000 to customers for losses from small-value fraudulent digital transactions.
• Draft guidelines to be issued on:
- Mis-selling of financial products.
- Loan recovery practices and recovery agents.
- Limiting customer liability in unauthorised electronic transactions.

• To support credit flow and ease of doing business:
- Collateral-free MSME loan limit proposed to be raised from ₹10 lakh to ₹20 lakh.
- Banks allowed to lend to REITs with prudential safeguards.
- Certain NBFCs exempted from registration and branch-opening approvals, subject to size and activity criteria.
About the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC)
• It was established in September 2016, under Section 45ZB (1) of the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934 (RBI Act).
• The Urijit Patel Committee had recommended the setting up of the MPC
• The MPC’s primary role is to set the Policy Rate required to achieve the inflation target.
• According to Section 42B (2) of the RBI Act, the MPC consists of:
- The Governor of RBI, who serves as the Chairperson, ex officio.
- The Deputy Governor of RBI is responsible for Monetary Policy, as a member, ex officio.
- One RBI officer nominated by the Central Board, as a member, ex officio.
- Three individuals appointed by the Central Government, as Members.
• Members appointed by the Central Government hold their positions for a term of four years or until further orders, whichever is earlier.
• According to Section 45ZA of the RBI Act, the inflation target is set at 4%, with an upper tolerance level of 6% and a lower tolerance level of 2%.
- If inflation exceeds 6% or drops below 2% for three consecutive quarters, it is deemed a failure to meet the target.

