Exercise KONKAN-2025
Context:
India hosted the annual bilateral maritime Exercise KONKAN-2025 on the west coast of India.
Exercise KONKAN-2025
- The Exercise is held between the Indian Navy and the UK Royal Navy.
- The bilateral naval exercise commenced on 5 October 2025 and will continue till 12 October 2025 off the western seaboard of India.
- The exercise aims to reaffirm the shared commitment of India and the United Kingdom towards maintaining secure, open, and free seas.
- This engagement exemplifies the Comprehensive Strategic Partnership envisioned under the India-UK Vision 2035.
- The exercise KONKAN was held for the first time in 2004.
- Phases of the Exercise: The harbour phase and the sea phase.
- Harbour phase: Will include professional interactions between naval personnel, cross-deck visits, sports fixtures, and cultural engagements. Additionally, Joint Working Group meetings and Subject Matter Expert Exchanges are also scheduled.
- Sea phase: Will encompass complex maritime operational drills focusing on anti-air, anti-surface, and anti-submarine exercises, flying operations and other seamanship evolutions.
- Participating Forces:
- The UK Carrier Strike Group (CSG-25), led by the aircraft carrier HMS Prince of Wales, is participating, along with assets from Norway and Japan, as part of the UK’s global deployment Operation Highmast.
- The Carrier Battle Group represents the Indian Navy centered around the indigenous aircraft carrier INS Vikrant, supported by other surface, sub-surface, and air combatants.
- After completing Exercise KONKAN-2025 on 12 October 2025, the UK Carrier Strike Group (CSG)-25 will hold a one-day exercise with the Indian Air Force on 14 October before continuing its deployment.
INS Androth
Context:
Recently, the Indian Navy commissioned INS Androth, the second Anti-Submarine Warfare Shallow Water Craft (ASW-SWC) at the Naval Dockyard, Visakhapatnam.
About INS Androth

- The ship is the second vessel in the Anti-Submarine Warfare Shallow Water Craft (ASW-SWC) series built by Garden Reach Shipbuilders & Engineers (GRSE).
- The first ship to be commissioned in this category was INS Arnala, earlier in June.
- It is named after Androth, the northernmost island of the Lakshadweep group, reflecting its historical and strategic maritime significance.
- The vessel is 77 metres long and has a displacement of about 1500 tonnes.
- It is designed for anti-submarine operations in coastal and shallow waters.
Key features of INS Androth
- It has over 80% indigenous content, highlighting India’s technological advancement and industrial capacity in defence manufacturing.
- The ship is fitted with advanced weapons, sensors, and communication systems to detect, track, and neutralise underwater threats effectively.
- It is powered by three waterjet propulsion systems driven by marine diesel engines, making it highly agile and manoeuvrable.
- The ship is capable of performing maritime surveillance, search and rescue, coastal defence missions, and low-intensity maritime operations (LIMO).
- The ship features modern machinery, automation systems, and advanced control technology for efficient performance.
Typhoon Matmo
Context:
Recently, Typhoon Matmo caused widespread evacuations and damage across the Philippines and southern China in early October 2025.
More on the News
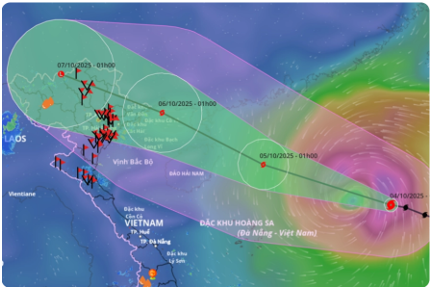
- The typhoon formed as a tropical depression over the western Philippine Sea on 1 October 2025 and developed into a tropical storm the next day.
- It made landfall in Isabela province on 3 October with sustained winds of about 130 km/h.
- More than 7,000 people were evacuated from flood and landslide-prone areas across the mountainous northern provinces.
- After moving across the South China Sea, it made landfall in Guangdong province on 5 October, prompting the evacuation of 150,000 residents.
- Meteorological agencies issued warnings for Guangxi and northern Vietnam as the storm moved westward.
Tropical Cyclones
- The terms “hurricane” and “typhoon” are regional names for tropical cyclones.
- All tropical cyclones share a common mechanism: they draw heat from warm ocean surface waters to power horizontal, rotating winds.
- Although tropical cyclones can be similar in size to synoptic cyclones, their energy source is different.
- Synoptic cyclones (mid-latitude storm systems) derive energy from weather fronts and jet streams, whereas tropical cyclones are fueled primarily by ocean heat.
- Regional Names:
- Hurricane: Atlantic Ocean and East Pacific Ocean
- Typhoon: West Pacific Ocean
- Cyclone: Indian Ocean and near Australia
UPI Usage Intensity
Context:
Telangana has recorded the highest per capita Unified Payments Interface (UPI) intensity among all the Indian States, according to a recent RBI Bulletin paper.
Findings of the RBI Study
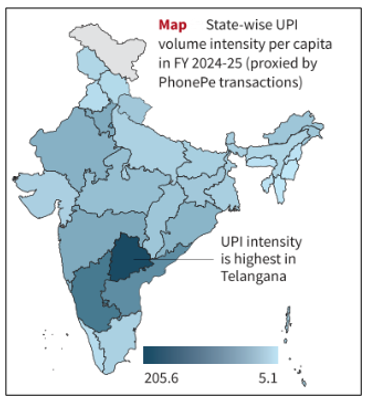
- The study assessed UPI usage intensity using PhonePe transaction data as a proxy, as the platform accounts for 58% of total UPI transaction volume.
- UPI is an Indian real-time, instant payment system that allows multiple bank accounts to be linked into a single mobile application for seamless fund transfers.
- Other states showing high UPI intensity include Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Delhi, and Maharashtra.
- In contrast, cash withdrawal intensity remains high in northeastern States, Kerala, Goa, and Delhi.
- Shift Towards Digital Payments:
- The rise of UPI has been identified as a major factor driving the decline in cash demand across the economy.
- This trend is evident from the steady fall in ATM cash withdrawals as a percentage of GDP.
- Changing Nature of Transactions:
- The average value of a single UPI transaction, also known as the “ticket size”, has been declining over time.
- The bulk of peer-to-merchant (P2M) transactions by volume now fall within the sub-₹500 value range.
- This indicates the growing use of UPI for low-value, everyday transactions, such as retail purchases and small payments.

