Samudra Pradakshina
Context:
Recently, the Defence Minister virtually flagged off Samudra Pradakshina, the world’s first tri-service all-women circumnavigation sailing expedition, from Mumbai.
About the Expedition
- The Minister described the voyage as a glowing symbol of Nari Shakti, representing the collective strength, unity, and jointness of the three Services.
- Over the next nine months, a 10-member all-women crew from the Indian Army, Navy, and Air Force will sail onboard the indigenously-built Indian Army Sailing Vessel (IASV) Triveni.
- It is the world’s first tri-service all-women circumnavigation sailing expedition, crossing the Equator twice, rounding the three great capes Leeuwin, Horn and Good Hope and covering all major oceans.
- The expedition will cover approximately 26,000 nautical miles on an easterly route starting from the Gateway of India in Mumbai.
- The crew is led by Lt Col Anuja Varudkar, has undergone 3 years of rigorous training and will conduct scientific research in collaboration with the National Institute of Oceanography.
- The crew will also make four port calls at Fremantle (Australia), Lyttelton (New Zealand), Buenos Aires (Argentina) and Cape Town (South Africa) and is scheduled to return to Mumbai in May 2026.
Chhath Puja Nomination for UNESCO Intangible Cultural Heritage List
Context:
Recently, the Union Ministry of Culture initiated consultations with international partners to seek the inclusion of Chhath Mahaparva in UNESCO’s Representative List of the Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity.
More on the News
- A proposal submitted by the Chhathi Maiya Foundation was forwarded to the Sangeet Natak Akademi (SNA), the nodal agency for UNESCO nominations.
- The Ministry of Culture convened a meeting in New Delhi, with diplomats from the UAE, Suriname, and the Netherlands to discuss the multinational nomination of Chhath Mahaparva to UNESCO’s Intangible Cultural Heritage List (2003 Convention).
- The Diplomats welcomed the initiative, recognising the festival’s significance for the Indian diaspora in their countries, and assured full support.
Chhath Puja
- It is an ancient Vedic festival dedicated to Surya (the Sun God) and Chhathi Maiya and one of the oldest festivals of India.
- Predominantly celebrated in Bihar, Jharkhand, Uttar Pradesh, and among the Indian diaspora worldwide.
- The festival is observed over four days, marked by strict rituals, fasting, and community participation.
- Known for its ecological ethos and emphasis on equality, the festival promotes sustainability, inclusivity, and community spirit, transcending caste, creed, and religion.
Intangible Cultural Heritage
- The United Nations, through UNESCO, defines intangible cultural heritage as the practices, expressions, knowledge, and skills that communities, groups, and individuals recognize as part of their cultural heritage and transmit from generation to generation.
- These living cultural traditions, which are constantly evolving and closely linked to a community’s identity and social cohesion, are expressed through various forms like oral traditions, performing arts, social practices, rituals, festive events, and traditional craftsmanship.
- Through UNESCO’s Intangible Cultural Heritage Lists, nations collaborate to protect and celebrate invaluable aspects of human heritage, ensuring their preservation for future generations.
- India currently has 15 elements inscribed on UNESCO’s Representative List of the Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity.
International Reference Classification of Occupations
Context:
Recently, the Government of India signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with the International Labour Organisation (ILO) for collaboration to develop the ‘International Reference Classification of Occupations’.
Key highlights of the MoU
- The MoU will facilitate youth in accessing global employment opportunities.
- Supported by a €650,000 contribution from India, it is India’s first direct funding agreement with the ILO, showcasing its leadership in multilateral cooperation.
- The initiative aims to enhance global competitiveness of Indian graduates and position India as a hub for high-quality, future-ready education and skilling.
- Under India’s 2023 Presidency, G20 leaders pledged to address global skill shortages arising from demographic deficits and rapid digitalisation by promoting skills-based migration pathways and endorsing an International Reference Classification of Occupations based on skills and qualification requirements.
- The agreement will help Indian workers to seamlessly integrate into global labour markets and reinforces India’s vision of becoming not just the skill capital of the world, but also a trusted source of talent for countries facing workforce shortages.
International Labour Organization (ILO)
- The ILO was established in 1919 by the Treaty of Versailles. Later, in 1945 ILO became the first specialised agency of the United Nations.
- It was founded on the conviction that universal and lasting peace can be established only if it is based on social justice.
- It is the only tripartite U.N. agency, since 1919 the ILO brings together governments, employers and workers of 187 Member States. India is one of the founding members of the organization.
- The ILO is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland.
Indian Scientists Map Milky Way’s Dusty Veil
Context:
Astronomers have mapped the invisible layers of cosmic dust that veil our Milky Way and redden the light of the stars.
About the Study
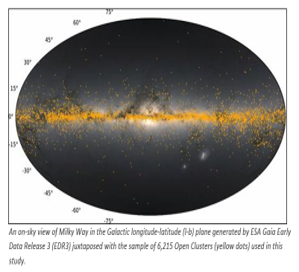
- Key Institution: Scientists from Aryabhatta Research Institute of Observational Sciences (ARIES), under the Department of Science & Technology (DST), Govt. of India, conducted a detailed study which may help trace the locations where the next generation of stars may be forming.
- Significance of Interstellar Dust: The Milky Way contains vast clouds of interstellar dust and gas that can block or dim starlight, a phenomenon called ‘extinction’ of starlight.
- Studying the distribution of dust helps scientists understand where stars form and the overall structure of the Galaxy.
- Methodology: Using data from 6,000+ open clusters (groups of stars), they mapped the distribution of interstellar dust across the Galactic disk (the thin plane of the Milky Way).
- Key Findings: The Milky Way’s interstellar dust is not evenly spread but forms a thin, wavy “reddening plane” lying slightly below the central Galactic plane, shifting up and down in a wave-like pattern, with dust being densest near Galactic longitude 41° and thinnest around 221°.
- The Sun is positioned about 50 light-years (15.7 parsecs) above this dusty layer, highlighting the uneven and dynamic structure of dust within our Galaxy.
- It also confirms that much of the dust is concentrated into a narrow band where new stars are actively forming.
- Future Application: The findings will allow astronomers to more accurately study the intrinsic properties of stars and distant galaxies by accounting for the obscuring effects of interstellar dust.
Early Retreat of Southwest Monsoon
Context:
The India Meteorological Department (IMD) has reported that the Southwest Monsoon (SWM) has begun its withdrawal from parts of west Rajasthan, marking the earliest retreat in a decade.
More on the News
- The SWM began withdrawing from western Rajasthan on September 14, three days earlier than the normal withdrawal date of September 17. In comparison, the withdrawal commenced on September 23 in 2024 and September 25 in 2023.
- The onset of the monsoon in 2025 was earlier than usual, occurring on May 24 instead of the normal date of June 1.
Criteria for the Monsoon Withdrawal
- Similar to the criteria for monsoon onset, the IMD realised the criteria for monsoon withdrawal including the following
- The development of an anti-cyclonic circulation over west Rajasthan at 1.5 km above mean sea-level.
- Dry or no rainfall over the region for five days.
- Reduction in moisture over the region up to the mid-troposphere.
Monsoon Trends Across States
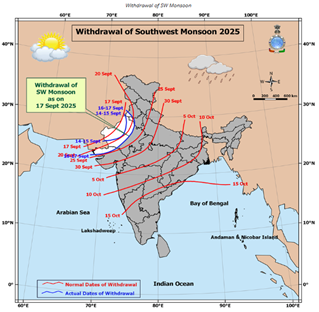
- According to IMD, as of September 15, the country had received 7% above normal rainfall during the season.
- Only four states all located in eastern and northeastern India recorded deficient rainfall.
- Meghalaya experienced the highest rainfall deficit at 44%, followed by Arunachal Pradesh at 40% deficit.
- In contrast, Rajasthan received 68% more rainfall than normal, the highest among all states, while the Union Territory of Ladakh recorded an exceptional 413% excess rainfall, the highest in the country.
- Apart from these, 12 states and Union Territories, including six in northwestern India, received excess rainfall ranging between 20 and 59% above normal, while 18 states and Union Territories recorded normal rainfall levels.

