Syllabus
GS-3: Awareness in the fields of IT, Space, Computer, robotics, etc. Achievements of Indians in science & technology; indigenization of technology and developing new technology.
Context:
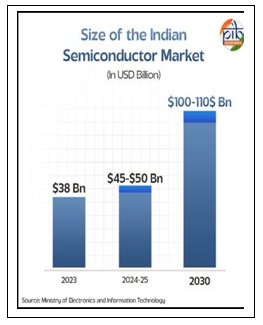
Recently, Industry estimates cited India’s semiconductor market is projected to grow from $38 billion in 2023 to $110 billion by 2030.
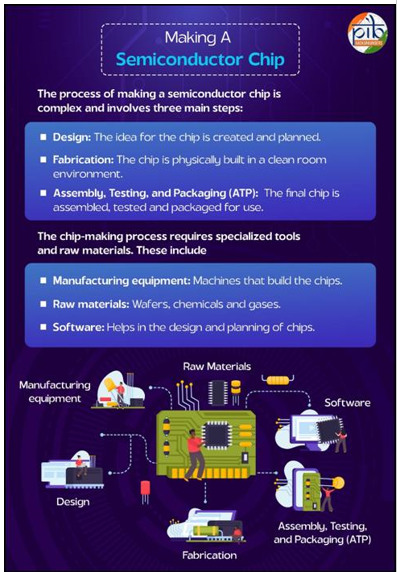
About Semiconductor
- A semiconductor is a material whose electrical conductivity lies between that of conductors and insulators, allowing it to act as either under different conditions
- These unique properties make semiconductors ideal for use in tiny electronic components that function as the brains of modern devices.
- Semiconductors are used to create electronic chips that control how devices function.
- Each chip contains millions or even billions of tiny switches called transistors that control electrical signals, similar to how brain cells work.
- Chips also contain other components such as resistors, capacitors, and wiring to help store, process, and transfer information.
Global Scenario of Semiconductor
- Currently, Taiwan, South Korea, Japan, China, and the United States dominate the global semiconductor industry.
- Taiwan alone produces over 60% of the world’s semiconductors and nearly 90% of the most advanced chips.
- Heavy dependence on a single region like Taiwan creates vulnerabilities in global supply chains due to risks like natural disasters, pandemics, and geopolitical tensions.
- India is emerging as a reliable and strategic partner in the effort to diversify global semiconductor supply chains.
India’s semiconductor market
• India’s entry into semiconductor manufacturing supports its ambition of becoming a global electronics hub and ensuring technological self-reliance.
• India is transitioning from a semiconductor-consuming nation to a global manufacturing hub, aiming to become a key player in the trillion-dollar global semiconductor value chain.
• India currently meets less than 9% of its semiconductor demand domestically and plans to increase this to 17% by 2026.
• India has the capacity to emerge as a key contributor to the 3 primary pillars of the semiconductor manufacturing supply chain
- Equipment: Leveraging a strong base of MSMEs to produce components for semiconductor equipment.
- Materials: India is a rich source of chemicals, minerals and gases which can be utilized by semiconductor supply chain companies.
- Services: R&D, Logistics and supply chain, with major talent in AI, big data, cloud computing and IoT.
• The global push for supply chain diversification underscores the strategic importance of India’s projected $100–110 billion semiconductor market by 2030.
India Semiconductor Mission (ISM)
- ISM was approved by the Union Cabinet in December 2021.
- The programme aims to provide financial support for investments in semiconductor fabrication, display manufacturing & chip design to strengthen India’s integration into global electronics value chains.
Schemes under ISM:
- Semiconductor Fabs Scheme
- Display Fabs Scheme.
- Compound Semiconductors and ATMP/OSAT Scheme
- Design Linked Incentive (DLI) Scheme
• ISM offers various skill development programs, training workshops, and certification courses to individuals interested in enhancing their skills and knowledge in the semiconductor field.
• SEMICON India programme: India plays a catalytic role in advancing ISM’s goals by enabling cross-border collaborations, promoting research commercialization, enhancing skill development, and showcasing India’s growing potential in the global semiconductor value chain.
- The platform brings together global industry leaders, policymakers, academia, and startups to foster investment, dialogue, and strategic partnerships.
Source:


