Context:
Recently, researchers at the Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA) in Bengaluru and their collaborator scientists have developed an innovative open-source tool to generate a comprehensive infrared star catalogue for the Adaptive Optics (AO) system of the upcoming Thirty Meter Telescope (TMT).
More on the News
- The tool creates an all-sky catalogue of Near Infrared (NIR) stars, essential for the TMT’s Adaptive Optics System (AOS) to produce high-quality images by counteracting atmospheric distortions.
The ground-based telescopes like TMT are sensitive to upper atmospheric disturbances which affect the quality of captured images. - The AOS system on TMT, known as the Narrow Field Infrared Adaptive Optics System (NFIRAOS), will be enhanced by a Laser Guide Star (LGS) facility which will project up to nine lasers into the sky to create artificial guide stars.
- However, these laser beams are affected by atmospheric turbulence. To correct these effects, the NFIRAOS requires feedback from three real stars, known as Natural Guide Stars (NGS).
- For optimal performance of NFIRAOS, a comprehensive catalogue of NIR stars is essential. However, no such catalogue exists that can reliably provide NGS for all sky regions, thus highlighting the critical need for the new tool developed by Indian researchers to create an all-sky NIR start catalogue.
About TMT:
- Location: Mauna Kea, Hawaii Island in the United States.
- It is an international project to build a telescope having a 30-metre diameter primary mirror made up of 492 precisely aligned optical and infrared mirror segments that will enable observations in deep space.
- It is collaboration involving institutions from the US, Japan, China, Canada and India.
- It will be the world’s most advanced and capable ground-based optical, near-infrared and mid-infrared observatory.
India’s Participation:
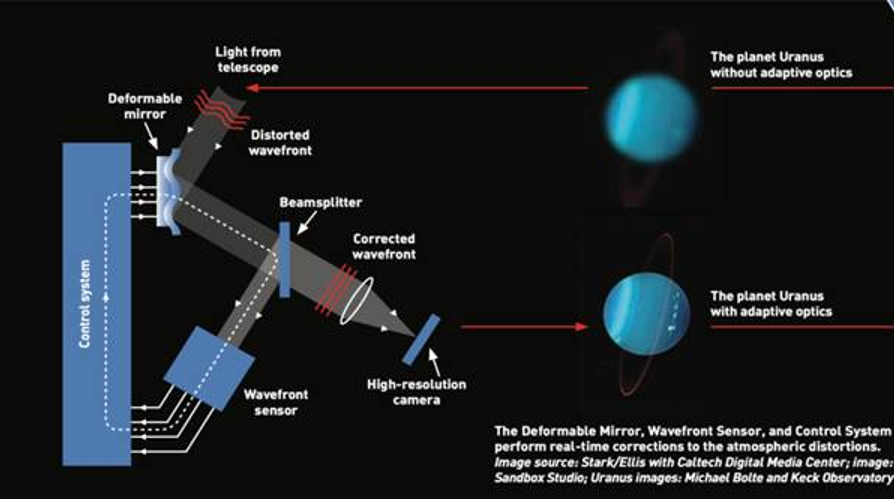
- Three key Indian institutes are involved: Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA) in Bengaluru, Inter-University Center for Astronomy and Astrophysics (IUCAA) in Pune, and Aryabhatta Research Institute for Observational Sciences (ARIES) in Nainital.
- The research was carried out at the India-TMT Coordination Center (ITCC), which is based at IIA in Bengaluru.
- ITCC also oversees India’s involvement in the TMT project.
A schematic diagram illustrating the working of an AO system in a telescope. (Image credits: TMT International Observatory)

