SYLLABUS
GS-1: Important Geophysical phenomena such as earthquakes, Tsunami, Volcanic activity, cyclones, etc.
GS-3: Disaster Management
Context: Recently, India launched Operation Sagar Bandhu to deliver urgent humanitarian assistance to Sri Lanka after Cyclone Ditwah caused severe floods, landslides, casualties and large-scale displacement.
More on the News
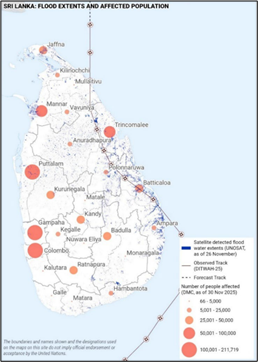
- The cyclone Ditwah made landfall in Sri Lanka on 28th November, before moving back over the Bay of Bengal.
- According to the WMO’s ESCAP (Economic Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific) panel, of which Sri Lanka is one of 13 member countries, the name was proposed by Yemen and is derived from Ditwah lagoon – a popular natural attraction on the island of Socotra in Yemen.
Operation Sagar Bandhu
- The Operation Sagar Bandhu reflects India’s approach of combining maritime capability with regional solidarity under the Neighbourhood First policy.
- The Indian Navy deployed INS Vikrant and INS Udaigiri to deliver relief materials, including essential supplies and emergency support.
India’s Key HADR Missions in Recent Years
- Operation Brahma (2025): It was a major humanitarian assistance and disaster relief (HADR) mission launched to assist Myanmar following a devastating 7.7-magnitude earthquake.
- Operation Dost (2023): It was a search and rescue operation initiated by the Government of India to aid Turkey & Syria following deadly earthquakes that struck on February 6, 2023.
- Operation Sahayata (2019): It was an operation conducted by the Indian Navy in response to Cyclone IDAI, which made landfall in Mozambique in March 2019.
- Operation Samudra Maitri (2018): It was launched to assist victims of the earthquake and tsunami in the Central Sulawesi Province of Indonesia.
- Operation Maitri (2015): It was a rescue and relief mission launched by India in response to the 2015 Nepal earthquake.
About Cyclones
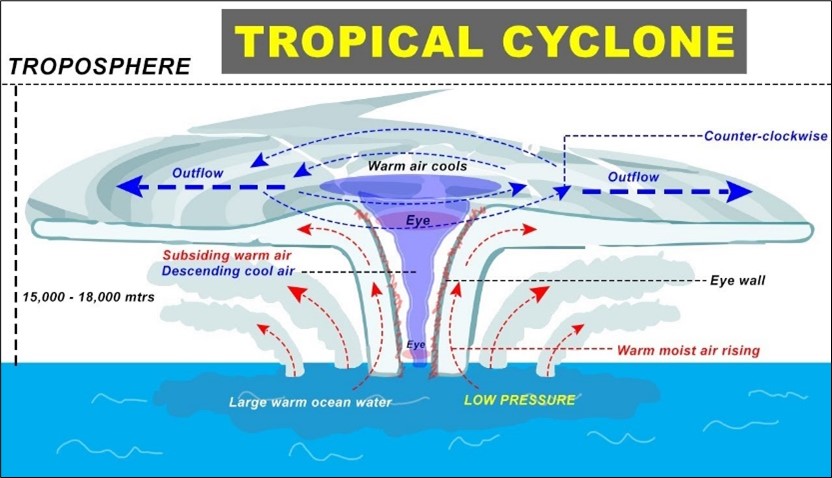
- A cyclone is a large, rotating air system around a low-pressure centre, bringing intense storms and severe weather.
- Its spiraling winds move inward and rotate anticlockwise in the Northern Hemisphere, while rotating clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere.
- Types: Classified into tropical and extratropical cyclones.
- Tropical Cyclone: Tropical cyclones are those which develop in the regions between the Tropics of Capricorn and Cancer.
- Tropical cyclones are Earth’s most intense storms, fueled by the “latent heat” released when evaporated ocean water condenses into liquid.
- They gain strength over warm waters, drawing energy that drives their high winds and heavy rains.
- They are known as hurricanes in the Caribbean Sea, the Gulf of Mexico, the North Atlantic Ocean, and the eastern and central North Pacific Ocean. In the western North Pacific, they are called typhoons.
- Extratropical Cyclone: Also known as mid-latitude cyclones, extratropical cyclones occur outside of the tropics. They typically form along fronts where cold and warm air masses meet.
- Types: Classified into tropical and extratropical cyclones.
- Cyclones are also categorized by wind speeds and the degree of potential destruction:
- Low Pressure: Wind speeds below 31 km/h
- Depression: Wind speeds between 31–61 km/h
- Cyclonic Storm: Wind speeds between 62–88 km/h
- Severe Cyclonic Storm: Wind speeds between 89–117 km/h
- Very Severe Cyclonic Storm: Wind speeds between 118–167 km/h
- Extremely Severe Cyclonic Storm: Wind speeds between 168–221 km/h
- Super Cyclone: Wind speeds exceeding 221 km/h
Naming of Cyclones
- Worldwide, there are six regional specialised meteorological centres (RSMCs) and five regional Tropical Cyclone Warning Centres (TCWCs) mandated for issuing advisories and naming of tropical cyclones.
- India Meteorological Department (IMD) is one of the six RSMCs to provide tropical cyclone and storm surge advisories to 13 member countries under the WMO/ESCAP Panel on Tropical Cyclones.
- 13 member countries: Bangladesh, India, Iran, Maldives, Myanmar, Oman, Pakistan, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Sri Lanka, Thailand, United Arab Emirates and Yemen
- The cyclone name list arranges member countries alphabetically, with each country’s suggested names listed alongside.
- Then these names are allotted to any cyclone, which takes place in the region, on a rotational basis regardless of which country proposed it.

