Syllabus:
GS-2: Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests, Indian diaspora
Context: Recently, India has received a waiver on the United States’ sanctions against Iran’s Chabahar port for a period of six months.
More on the News
- The original sanctions waiver granted in 2018 exempted India’s development activities at Chabahar from sanctions to support Afghanistan’s reconstruction.
- In 2025, the US revoked this waiver as part of a maximum pressure policy on Iran under President Trump’s administration.
- The latest U.S. decision to extend the waiver means that supplies to Afghanistan, especially essential items like food grains and medical products, can still be sent through Chabahar.
Strategic Importance of Chabahar Port
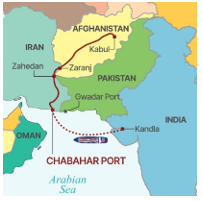
- It is located in southeastern Iran on the Arabian Sea, Chabahar Port provides India with its only direct maritime access to Afghanistan and Central Asia bypassing Pakistan.
- It is a vital component of India’s regional connectivity strategy and plays a key role in India’s Afghanistan and Central Asia policy.
- The port facilitates the International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC), which aims to connect the Indian Ocean and Persian Gulf to the Caspian Sea and onward to Northern Europe via Russia, significantly reducing cargo transit time and enhancing trade logistics.
Geopolitical Implications of the Waiver
- Pragmatic Accommodation: The waiver reflects a nuanced US policy accommodating India’s strategic interests despite broader sanctions on Iran.
- Countering Assertive China: Chabahar enables India to counterbalance China’s growing influence in the region, especially through China’s investment in Pakistan’s Gwadar Port.
- Connecting Central Asia: The port strengthens India’s connectivity with mineral rich Central Asian states, augmenting its geopolitical leverage.
- Bypassing Pakistan: The port enables India to support Afghanistan’s reconstruction and send Development aid without reliance on the land route through Pakistan.

