SYLLABUS
GS-3: Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources, growth, development and employment and Science and Technology- developments and their applications and effects in everyday life.
Context: Recently, India Post Payments Bank has launched its Aadhaar-based face authentication facility for customer transactions, which is expected to make digital banking more secure and convenient.
Aadhaar-based Face Authentication facility
• This Facility enables customers to perform banking transactions using facial recognition, eliminating the need for physical biometric inputs like fingerprints or OTPs.

• The face authentication feature was developed under the framework of UIDAI (Unique Identification Authority of India).
Key Benefits of IPPB’s Face Authentication Feature
• Inclusive Banking for the elderly, differently-abled, and individuals with worn fingerprints.
• Secure Aadhaar Authentication without dependency on OTP or fingerprint sensors.
• Fast & Contactless Transactions for a smoother customer experience.
• Safe Banking During Health Emergencies, where physical contact may be risky.
• Support for All Banking Services, including account opening, balance inquiry, fund transfers, and utility payments.
India Post Payments Bank (IPPB)

• IPPB was established in 2018 under the Department of Posts, Ministry of Communications, with 100% equity owned by the Government of India.
• IPPB aims to provide accessible, affordable, and reliable banking services to all Indians, with a special focus on rural and underserved areas.
• It leverages the extensive postal network to bring banking services to the doorstep of every citizen, supporting the government’s financial inclusion objectives.
• IPPB are registered as a public limited company under the Companies Act of 2013 and is licensed under Section 22 of the Banking Regulation Act of 1949.
Legislations Governing IPPB
- The Banking Regulation Act of 1949.
- The Reserve Bank of India Act of 1934.
- The Foreign Exchange Management Act of 1999.
- The Payment and Settlement Systems Act of 2007.
Key Features of IPPB
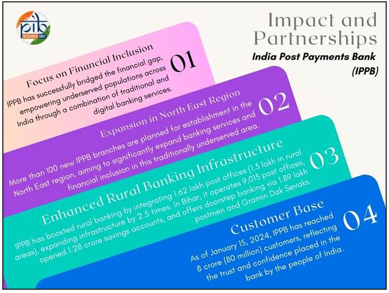
• Extensive Network: IPPB capitalises on India Post’s vast network of over 155,000 post offices, with 135,000 located in rural areas.
• Doorstep Banking: Over 300,000 postmen and Gramin Dak Sewaks provide banking services at customers’ doorsteps using smartphones and biometric devices, especially beneficial for those in remote areas.
• Digital Focus: IPPB offers a seamless, paperless, cashless, and presence-less banking experience through digital platforms, integrating core banking systems with smartphones and biometric devices.
• Accessibility: Banking services are available in 13 regional languages, ensuring inclusivity for India’s diverse population.
• Low-Cost Model: IPPB focuses on frugal innovation to keep its services affordable, especially for economically weaker sections of society.
Innovation and Partnerships
• Fincluvation Initiative: A platform launched to collaborate with fintech startups, co-create solutions, and innovate for financial inclusion.
• WhatsApp Banking Services: Launched in March 2023 in collaboration with Airtel, enabling customers to access banking services via WhatsApp with plans for multi-language support.
• Ria Money Transfer Partnership: Provides international inward money transfer services, initially available at over 25,000 Post Office locations.

Source
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2151308
https://cleartax.in/glossary/payment-banks
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressNoteDetails.aspx?NoteId=152040&ModuleId=3

