SYLLABUS
GS-1: Important Geophysical phenomena such as earthquakes, Tsunami, Volcanic activity, cyclone etc.
GS-3: Disaster and Disaster Management.
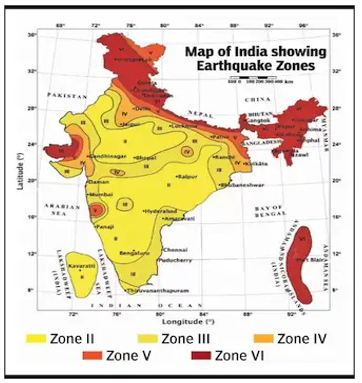
Context: The Bureau of Indian Standards has released an updated seismic-hazard map by revising the Earthquake Design Code, 2025, that places the entire Himalayan arc in the newly defined Zone VI (highest risk) for earthquakes.
About New Seismic Zonation Map
- Aim: The revision aims to account properly for long-locked fault segments, especially in the central Himalaya, that had not ruptured in a surface-breaking event for nearly two centuries but continues to accumulate stress.
- Increased Coverage: Under the new map, approximately 61% of the country’s area now falls under moderate to high seismic hazard zones, up from earlier estimates.
- Removed terrain inconsistencies: The uniform re-classification corrects prior inconsistencies where similar Himalayan terrain was divided between different zones, despite sharing the same tectonic threats.
- Internationally accepted Standards: The new map is based on probabilistic seismic hazard assessment methods that include data on active faults, potential earthquake magnitudes, ground shaking patterns, and underlying geology.
- Updated seismic-resistant design standards: The revised norms urge that all new buildings and infrastructure projects — including critical facilities such as hospitals, schools, bridges and public buildings.
Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS)
• Indian Standards Institution (ISI) was established in 1947 and registered under the Societies Registration Act, 1860 later, ISI was renamed as Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS).
• The Scheme formally launched by ISI in 1955-56, enabled it to grant licences to manufacturers producing goods in conformity with Indian Standards and to apply ISI Mark on their products.
- BIS allot the ISI mark to any product as a third-party guarantee after ensuring its quality, reliability and safety.

• The Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) came into existence under the BIS Act, 1986. The standards established by the Bureau shall be the Indian Standard.
• A new Bureau of Indian Standards Act, 2016 which was brought into force in 2017, established BIS as the National Standards Body of India.
• BIS is Headquartered at New Delhi.

