Dental Amalgam Set to Be Phased Out by 2034
Context:
Recently, the Sixth Conference of the Parties (COP-6) to the Minamata Convention on Mercury, held in Geneva, decided to phase out mercury-based dental amalgam globally by 2034.
More on the News

- This decision was adopted by 153 parties to the Minamata Convention on Mercury.
- The World Health Organization considers mercury one of the top 10 chemicals of major public health concern, calling it “toxic to human health”.
- This phase-out marks a historic milestone in international efforts to eliminate mercury use, particularly in dentistry.
- This move aligns with the convention’s long-term objective of completely eliminating mercury from healthcare and industrial applications.
- This issue of dental amalgam was debated over three COP sessions before a final consensus was reached during COP-6.
About Dental Amalgam
- Dental amalgam is a mixture of liquid mercury and silver used for filling tooth cavities.
- It is a durable and cost-effective restorative material that is approximately 50% mercury by weight.
- Mercury-free alternatives include composite resins, glass-ionomer cements, resin-modified ionomers, ceramics, and gold restorations.
37th Meeting of the Parties to the Montreal Protocol (MOP37)
Context:
Recently, the 37th meeting of the Conference of the Parties to the Montreal Protocol (MOP37) was held in Nairobi, Kenya, from 1 November to 7 November 2025.
More on the News
- This meeting marked the 40th anniversary of the Vienna Convention for the Protection of the Ozone Layer, celebrating global cooperation in protecting the ozone layer.
- The Vienna Convention for the Protection of the Ozone Layer is a 1985 framework treaty that promotes international cooperation to protect the ozone layer through research, information exchange, and the adoption of legislative measures.
- The parties adopted 20 decisions, including further analyses on the HFC-23 emission gap.
Key Highlights of the Meeting
- HFC Emissions Discrepancies: A primary focus was on the “massive discrepancy” between reported and atmospherically monitored emissions of HFC-23 (a potent greenhouse gas), leading to a decision to enhance regional atmospheric monitoring of controlled substances.
- Multilateral Fund (MLF) Replenishment: The terms of reference for the study on the 2027-2029 replenishment of the MLF were adopted.
- Management of Used Refrigerants: Parties agreed on a mandate for the Technology and Economic Assessment Panel (TEAP) to conduct a study on the quantities and options for managing used and unwanted controlled substances, including those nearing their end-of-life.
- Halons in Aviation: A decision was reached on the continued use of halon 1301 in the aviation industry, encouraging parties to facilitate the import and export of recycled halons for fire suppression needs and inviting information on new alternatives.
About the Montreal Protocol
- The Montreal Protocol is an international treaty that successfully phased out the production and consumption of ozone-depleting substances (ODS) to protect the Earth’s protective ozone layer.
- The Montreal Protocol was adopted in 1987. It is considered one of the most successful environmental agreements because it has achieved universal ratification and has led to a significant reduction in ODS, which helps protect the public from harmful UV radiation.
India to Boost Neodymium Production
Context:
Recently, the Indian Rare Earths Limited (IREL), under the Department of Atomic Energy, announced plans to raise neodymium production to 500 tonnes by FY27.
More on the News

- This expansion marks a ninefold increase from the 40 tonnes produced last year, during the peak of the global rare-earth supply crisis.
- The move comes as China imposed export restrictions on several rare earth elements and magnets, compelling countries to strengthen domestic production.
- IREL operates extraction facilities in Odisha and refining units in Kerala, producing eight of the 17 rare earth elements, including neodymium, praseodymium, and dysprosium.
- The company’s production of neodymium and praseodymium is expected to double within a year, driven by indigenous engineering advancements.
- India currently has the third-largest reserves of REEs, estimated at 6.9 million metric tons. However, its current production is less than 1% of the global supply.
- The expansion aligns with the National Critical Mineral Mission (NCMM), which aims to strengthen critical mineral value chains through an expenditure of ₹16,300 crore and an expected investment of ₹18,000 crore from FY25–FY31.
About Neodymium
- Neodymium is a silvery-white rare-earth metal, known for its role in manufacturing high-strength permanent magnets.
- It is primarily used in electric vehicle motors, wind turbines, defence systems, electronics, and optical instruments.
- The element is found in monazite and bastnasite minerals, with major deposits located in China, India, Australia, and Brazil.
- Neodymium magnets are among the strongest permanent magnets available, making them vital for compact and energy-efficient technologies.
18th Urban Mobility India (UMI) Conference & Exhibition 2025
Context:
Recently, the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs organised the 18th Urban Mobility India Conference & Exhibition 2025 in Gurugram, Haryana.
More on the News
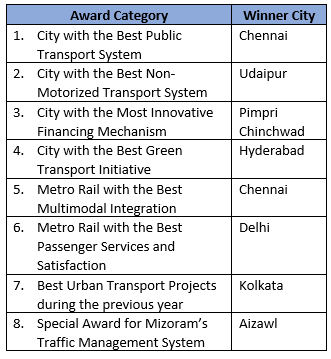
- The conference was held under the theme “Urban Development and Mobility Nexus”, focusing on the integration of sustainable urban planning and transport development.
- The Conference is an international forum to deliberate on important issues and challenges related to urban transport.
- The logo and website of the PM e-Bus Sewa Scheme were launched during the valedictory session, marking a major step toward sustainable public transport.
- The three-day conference concluded with the distribution of awards in 8 different categories of Urban Transport.
- It was also announced that the 19th Urban Mobility India Conference & Exhibition 2026 will be held in Bhubaneswar, Odisha, in October 2026.
About the Urban Mobility India (UMI) Conference
- The UMI Conference is an annual international forum organised by the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs to deliberate on urban transport challenges and sustainable mobility solutions.
- It serves as a platform for central, state, and city-level officials, along with national and international experts, to share experiences and promote best practices in urban mobility.
- The 17th edition was held in Gujarat, with participation from around 1,500 delegates from India and abroad.
- The official website of the UMI Conference provides information on registration, updates, and publications related to urban transport initiatives in India.
155th Birth Anniversary of Chittaranjan Das
Context:
Recently, the Lok Sabha Speaker paid tribute to freedom fighter Deshbandhu Chittaranjan Das on his 155th birth anniversary in New Delhi.
Deshbandhu Chittaranjan Das

- Chittaranjan Das was born on 5 November 1870 in Central Calcutta.
- He travelled to England and joined the Middle Temple to study law.
- He was called to the English Bar in 1893 and returned to India in 1894 to practice at the Calcutta High Court.
- His national prominence rose after his successful defence of Aurobindo Ghose in the Alipore Bomb Case (1908).
- He contributed to Bengali literature by writing works such as Sagar-Sangit, Antaryami and Kishor-Kishori.
- His political journey began as a Congress delegate in 1906 and expanded his role after 1917, when he presided over the Bengal Provincial Conference.
- He opposed the Montagu–Chelmsford Reforms (1918) and strongly criticised the Rowlatt Act (1919).
- He supported Mahatma Gandhi’s call for Satyagraha and later joined the Non-Cooperation Movement.
- He founded the National University at Dhaka in 1921 as part of the movement.
- After differences over council entry, he co-founded the Swaraj Party on 31 December 1922 with Motilal Nehru.
- He became the first Mayor of Calcutta in 1923 under the Calcutta Municipal Act. He introduced major civic reforms in education, health, sanitation and public transport.
- He appointed Subhas Chandra Bose as the Chief Executive Officer of the Calcutta Corporation.
- He promoted the Forward Publishing Company, which launched the influential daily newspaper Forward.
- He worked to strengthen Hindu–Muslim unity and framed the Bengal Pact advocating communal harmony.
- He presided over the Bengal Provincial Conference at Faridpur in 1925 and spoke on India’s role in global peace and the Commonwealth.
- Chittaranjan Das passed away on 16 June 1925 at Darjeeling, where he had gone to recover from deteriorating health.
Ideology of Deshbandhu Chittaranjan Das
- He believed that India’s freedom must be achieved through self-sacrifice, moral courage and spiritual strength inspired by Satyagraha.
- He supported constitutional obstruction from within legislatures until he later embraced the Non-Cooperation Movement.
- He believed that national unity required Hindu–Muslim cooperation and worked towards building harmonious relations between communities.
- He advocated Swaraj through constructive politics, strong civic institutions and decentralised administration.
Exercise Mitra Shakti Xi – 2025
Context:
India is hosting the eleventh edition of the India–Sri Lanka joint military exercise Mitra Shakti 2025.
More on the News
- The exercise Mitra Shakti 2025 commenced at the Foreign Training Node in Belagavi, Karnataka, on 10 November 2025 and will continue till 23 November 2025.
- The objective of this annual exercise is to jointly rehearse sub-conventional operations under Chapter VII of the United Nations mandate.
- The exercise incorporates the use of drones, counter-unmanned aerial systems and helicopters for operational drills.
- The exercise aims to enhance interoperability and reduce operational risks while aligning with UN peacekeeping objectives.
- Both sides will exchange views on combat skills and share best practices to strengthen defence cooperation further.
- The exercise reflects the strong bilateral relations and mutual trust between India and Sri Lanka.
- The inaugural edition of the Mitra Shakti exercise was held in Pune, India, in 2012.
Other Key Exercises between Sri-Lanka and India
- Sri Lanka–India Naval Exercise (SLINEX), an annual bilateral maritime drill enhancing interoperability since 2005.
- The 2024 edition of SLINEX was conducted off the coast of Visakhapatnam, India, from December 17 to 20, 2024.

