Minimum Support Prices (MSP) for Rabi Crops
Context:
Recently, the Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs approved Minimum Support Prices (MSP) for Rabi Crops for Marketing Season 2026-27.
More on the News
- The sharpest hike has been announced for safflower, with an increase of ₹600 per quintal, followed by lentil (masur) at ₹300 per quintal.
- The MSP of rapeseed and mustard has been raised by ₹250 per quintal, gram by ₹225 per quintal, barley by ₹170 per quintal, and wheat by ₹160 per quintal.
About the Minimum Support Price (MSP)
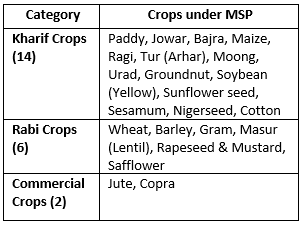
- MSP introduced in 1966-67 is a price fixed by the Government of India to protect the producers – farmers – against excessive falls in price during bumper production years.
- Government announces MSPs for 22 mandated crop and Fair Remunerative Price (FRP) for Sugarcane (Total 23).
- MSP is determined by the Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs (CCEA), Government of India.
- Recommendations are provided by the Commission for Agricultural Costs and Prices (CACP), after considering the views of State Governments and Central Ministries/ Departments concerned.
- MSP is declared before the sowing season of major agricultural commodities.
Home Ministry Advisory on FCRA Renewal Applications
Context:
The Union Home Ministry directed all NGOs to submit application for the renewal of their Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Act (FCRA) registration at least four months before expiry of their current certificate.
More on the News

- Many NGOs have been submitting renewal applications less than 90 days before expiry.
- This delay prevents adequate scrutiny and security clearance, leading to situations where:
- Certificates expire before renewal is processed.
- NGOs are unable to receive or utilise foreign contributions during the interim.
- The sole purpose of the Ministry is to ensure timely scrutiny of applications and prevent disruption in NGO activities.
- Legal Requirement (Section 16(1), FCRA 2010):
- NGOs must apply for renewal within six months prior to the expiry of the certificate.
- The Central Government ordinarily renews the certificate within 90 days from receiving the application.
National Dhanwantari Ayurveda Awards 2025
Context:
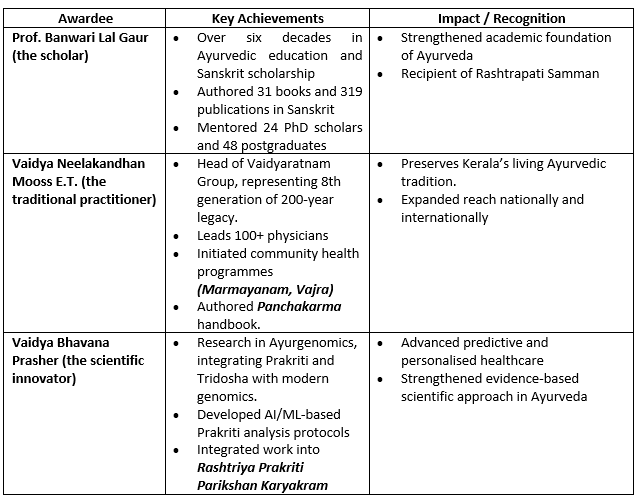
Recently, the Ministry of Ayush conferred the National Dhanwantari Ayurveda Awards 2025 on Prof. Banwari Lal Gaur, Vaidya Neelakandhan Mooss E.T., and Vaidya Bhavana Prasher, in recognition of their outstanding contributions to the classical, traditional, and scientific domains of Ayurveda.
About the National Dhanwantari Ayurveda Awards
- Instituted by the Ministry of AYUSH, among the highest honors in the field of traditional Indian medicine.
- It recognises excellence across three dimensions of Ayurveda: scholarship, living tradition, and scientific innovation.
About the Awardees
International Day of Non-Violence 2025
Context:
The International Day of Non-Violence, celebrated annually on 2nd October, marks the birth anniversary of Mahatma Gandhi, a global beacon of peace and non-violence.
More on the News
- In India, the day is celebrated as Gandhi Jayanti, while globally it is observed as the International Day of Non-Violence, following a 2007 United Nations resolution supported by over 140 nations.
- This dual observance reflects a unique blend of national memory and universal message for humanity.
About Mahatma Gandhi: Life and Philosophy
- Mahatma Gandhi was an Indian lawyer, politician, social activist, and writer who became the leader of the Indian Independence Movement against British rule.
- A central principle of his philosophy was ahimsa (Nonviolence), meaning “non-injury” or “compassion,” which advocated non-violence in thought, word, and action towards all living beings.
- He coined the term “satyagraha”, from satya (truth) and agraha (insistence), representing his philosophy of non-violent resistance.
- This principle guided major movements in India, including the Dandi March (1930) and the Quit India Movement (1942), demonstrating that moral force could mobilize millions without violence.
- Mahatma Gandhi transformed Ahimsa into a powerful tool of political resistance through Satyagraha, inspiring global leaders like Nelson Mandela and Martin Luther King Jr. in their civil rights movements.
Acoustic Vehicle Alerting System (AVAS)
Context:
In a step to curb road accidents involving electric vehicles, the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH) has proposed making the Acoustic Vehicle Alerting System (AVAS) mandatory for electric cars, buses, and trucks.
More on the News
- All new electric vehicle models, including passenger and goods vehicles, manufactured after October 1, 2026, must be fitted with AVAS to meet audibility requirements.
- For existing models, the cutoff date is October 1, 2027, after which AVAS installation will also be mandatory.
Why AVAS is Needed
- The AVAS is a device that generates sound when a vehicle is moving at speeds up to 20 kmph to alert pedestrians and other road users.
- This measure is significant because electric vehicles moving at low speeds emit minimal sound, which increases the risk of accidents.
- Pedestrians and cyclists often cannot detect approaching EVs due to their silent operation.
- With the growing adoption of EVs, especially two and three-wheelers, the need for an alerting system has become significant.
Applicability to Two and Three-Wheelers
- The draft notification currently excludes two-wheelers, three-wheelers, e-rickshaws, and e-carts from the AVAS requirement.
- Analysts have raised concerns, suggesting all electric vehicles should be fitted with AVAS, especially those operating in remote areas, to reduce accident risks.
E-Vehicles in India
- The Ministry highlighted that the number of electric vehicles has increased substantially, with 19.50 lakh units sold in 2024, forming 7.44 percent of total vehicle sales.
- In India, the share of electric vehicles in overall sales has grown from01 percent in 2014-15 to 7.31 percent in 2024-25, with 56.75 lakh registered vehicles by February 2025.
India’s First Indigenous IBR Vaccine
Context:
Recently, Indian Immunologicals Limited (IIL) has launched India’s first indigenously developed glycoprotein E (gE) deleted DIVA marker vaccine against infectious bovine rhinotracheitis (IBR).
More on the News
- The vaccine, named Raksha-IBR, aims to address infertility, abortions, and reduced milk productivity associated with the disease.
- The vaccine was developed after years of joint research between scientists of IIL and the National Dairy Development Board.
- The launch event coincided with the diamond jubilee celebration of the National Dairy Development Board in Anand, Gujarat, on September 27.
- Marker vaccines such as Raksha-IBR allow veterinarians to differentiate between infected and vaccinated animals (DIVA).
- India did not have any vaccine or specific treatment for IBR until now, making this development significant for animal health and dairy productivity.
About the Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis (IBR)
- IBR is endemic in India and is caused by the Bovine Herpes Virus type 1 (BHV-1).
- BoHV-1 is a member of the Varicellovirusgenus of the alphaherpesvirinae subfamily.
- The disease is transmitted through aerosol routes and affects the reproductive systems.
- It is also transmitted by infected semen from bulls to milch animals.
- Impact: Infertility, abortions, and lower milk productivity.

