Syllabus:
GS-3: Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization of resources, growth, development and employment; Effects of liberalization on the economy, changes in industrial policy and their effects on industrial growth.
Context:
The United States has imposed tariffs on a wide range of Indian merchandise exports, raising them to as high as 50%.
More on the News
- The 50% tariff, has been charged on America’s accusations that India’s crude oil purchase from Russia, which makes India one of the US’s highest tariffed countries on lines with Brazil.
- The US is the largest export partner for India, accounting for 18% of total exports, equivalent to about 2.3 per cent of India’s GDP.
- Think tank Global Trade Research Initiative estimates India’s exports to the US may drop to $49.6 billion from $87 billion in 2024–25.
Implications of the US Tariffs on Varied Sectors.
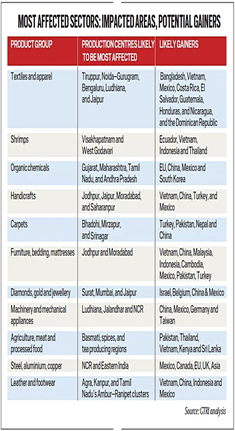
- Shrimps: According to data from the Ministry of Commerce and Industry in 2024-25, India exported 32.4% of its total shrimp exports to US. The earlier 10% countervailing duty on Indian shrimp has now been raised to a total of 60%.
- Diamonds, Gold, and Jewellery: India’s exports of diamonds, gold, and jewellery to the U.S. accounted for 40% of the sector’s total exports in 2024-25 and now face tariffs raised from 2.1% to 52.1%.
- Textiles and Apparel: The U.S. accounts for 35% of India’s apparel exports, and the sector now faces a 63.9% tariff, up from the previous 13.9% making it one of the worst-hit sectors.
- Carpets: India exported $1.2 billion worth of carpets to the U.S. in 2024-25, accounting for 58.6% of total carpet exports, with tariffs rising from 2.9% to 52.9%.
- Other Sectors: Other significantly affected sectors include handicrafts, leather and shoes, furniture and bedding, and agricultural products such as basmati rice, spices, tea, pulses, and sesame.
- Uncompetitive in the US Market: Nearly 66% of India’s exports to the U.S. now face a 50% tariff, a blow to labour-intensive industries that rely heavily on US demand rendering these export uncompetitive.
Exempted Items from 50% Tariffs
- About 30% of India’s exports to the U.S., worth $27.6 billion in FY25, will remain duty-free as pharmaceuticals, electronics, and petroleum products are exempt from U.S tariffs.
- Metals: It includes unwrought antimony, nickel, zinc, chromium, tungsten, platinum, palladium, gold dore, gold coins, technically-specified natural rubber, coral, echinoderms and cuttlebone are also exempt.
- Other exempted items include refined petroleum fuels and products ($4.1 billion in 2024-25), as well as books, brochures, plastics, cellulose ethers, ferromanganese, ferrosilicon manganese, ferrochromium and computing gear such as motherboards and rack servers.
Way Forward
- Boosting Home Demand: Planned Goods and Services Tax (GST) cuts on essentials are expected to lower household costs, stimulating domestic consumption.
- Government Support and Policies: Implement targeted subsidies, duty drawback, or reimbursement schemes and provide temporary financial aid to protect jobs in affected sectors.
- Diversifying Export Destination: Fast-track FTAs with the EU, UK, and Gulf; explore new markets in Africa and Latin America for textiles, gems, and marine products.
- Innovation for Global Standard: Encourage technology adoption, product innovation, and value addition in textiles and gems to strengthen global standing.

